Key Takeaways
Complete, accurate, and structured behavioral data is valuable for improving customer experience (CX). It can provide insights into customer interactions, preferences, and habits through various activities like website visits, social engagements, and purchase history.
It's collected from sources like CRM systems, websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms. It is categorized into first-party, second-party, and third-party data, each with its own benefits and uses.
Utilizing behavioral data enables businesses to personalize marketing campaigns, identify and optimize customer journey friction points, develop forecasting and digital benchmarks, and boost engagement, although it must be managed with stringent privacy and ethical considerations.
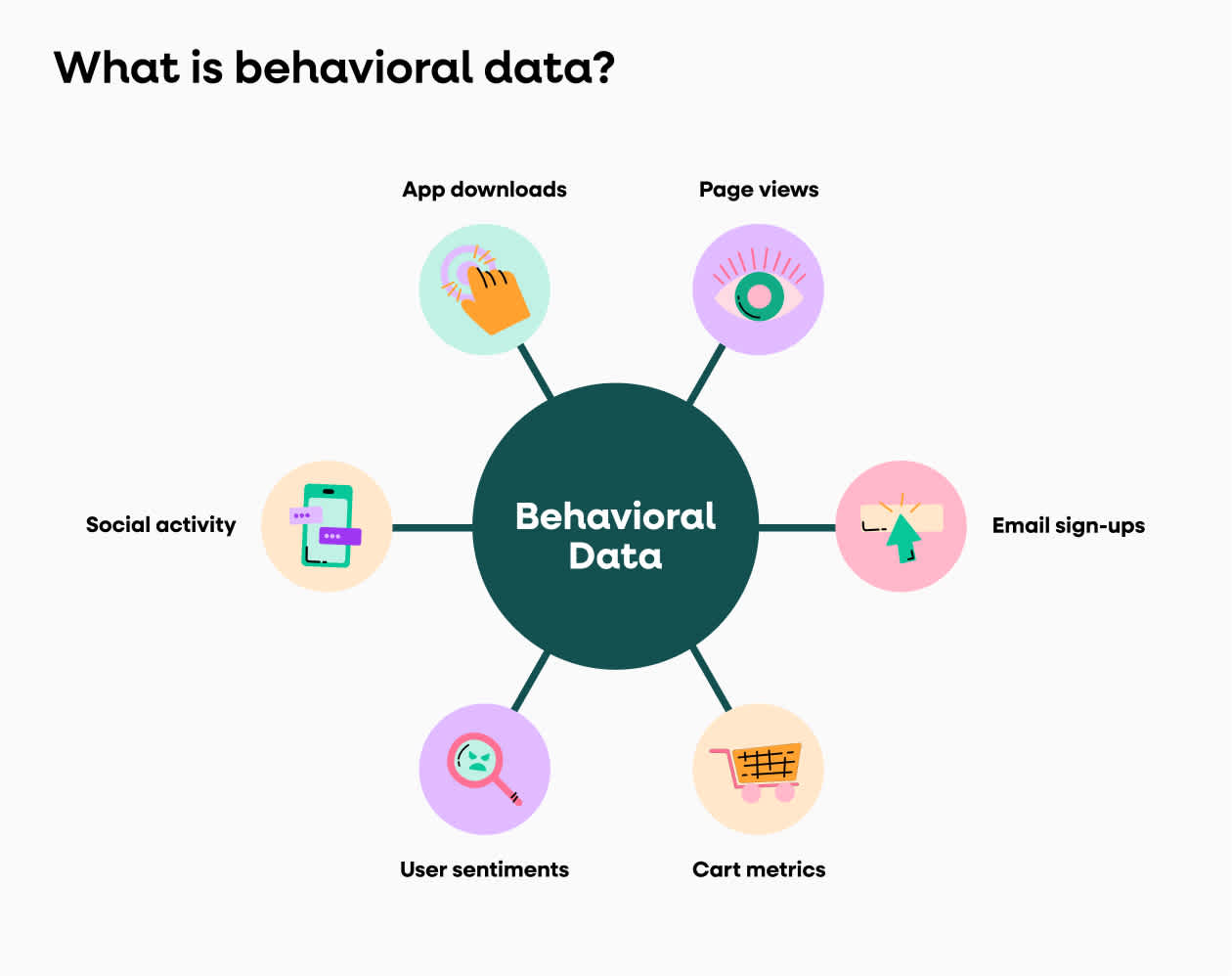
What is behavioral data?
Behavioral data describes how customers, applications, or systems interact with your business: page views, sign-ups, clicks, logins, purchases, calls, or even user frustrations can be captured via websites, apps, email, social media, CRM, and sensors. These context-rich signals power personalization, advanced analytics, and AI-driven predictions.
Alongside demographic data, this data is generated by user interactions online, such as:
website views
newsletter sign-ups
shopping cart activities
sentiment signals, like rage clicks
social media engagements
It’s like a digital breadcrumb trail that customers leave behind, revealing their preferences and habits and allowing businesses to significantly improve the value of their existing systems, such as analytics, personalization, product forecasting, A/B testing, and marketing automation.
Scale with behavioral data insights
Gauge your team’s behavioral data readiness and find practical steps to elevate your data approach.
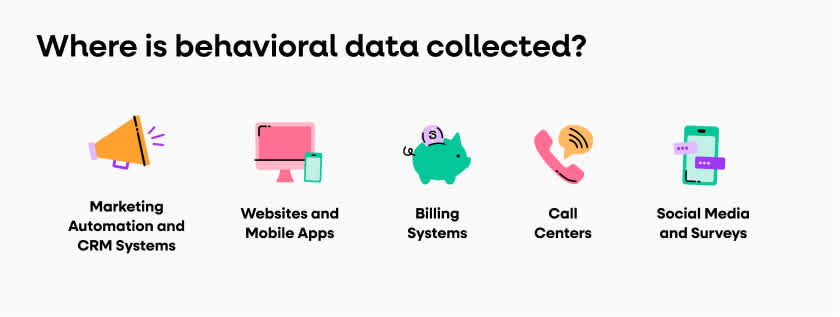
Where is behavioral data collected?
Businesses leverage a variety of digital platforms and tools to gain a comprehensive understanding of customer behavior. These systems not only track user actions but also provide valuable insights into preferences and experiences.
Marketing automation and CRM systems: Collect data on user interactions, purchase history, and preferences.
Websites and mobile apps: Utilize pixels and tracking technologies to capture browsing behaviors and user engagement metrics.
Billing systems: Reveal customer payment patterns and preferences, adding a financial dimension to user behavioral data.
Call centers: Offer direct insights into customer inquiries and service experiences.
Social media and surveys: Enrich understanding by capturing user preferences and feedback directly from the source.
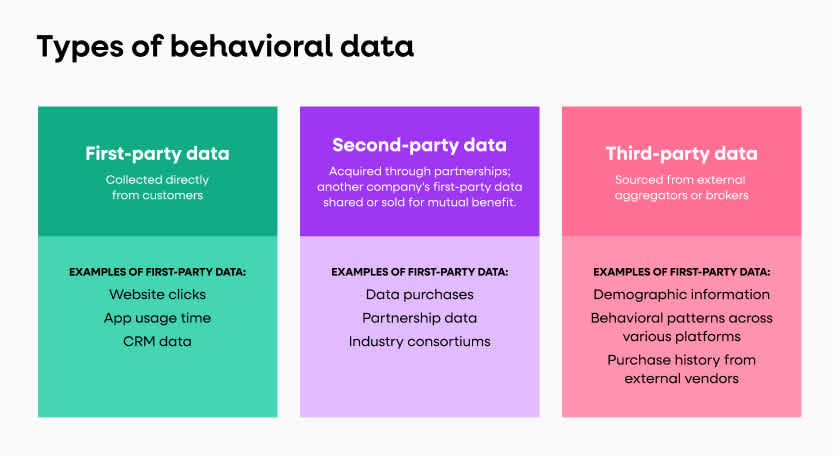
Types of behavioral data
Three main types of behavioral data exist, each with a unique role in decoding customer behavior:
First-party data: Collected directly from customers, offering unparalleled reliability and insight into customer behaviors, preferences, and actions. This builds a foundation for personalized marketing and customer experience enhancement derived from direct interactions like purchases, abandoned carts, and website visits.
Examples of first-party data:
Website clicks
App usage time
CRM data
Second-party data: Acquired through partnerships, second-party data is another company's first-party data shared or sold for mutual benefit. This data extends marketing reach by accessing insights from similar customer bases, therefore enriching understanding without direct collection.
Examples of second-party data:
Data purchases
Partnership data
Industry consortiums
Third-party data: Sourced from external aggregators or brokers, this data provides a broad view of market trends and consumer behavior across various sources. It is valuable for broad market analysis and identifying general trends, albeit less directly relevant to individual customer actions.
Examples of third-party data:
Demographic information
Behavioral patterns across various platforms
Purchase history from external vendors
Behavioral analytics tools turn data into action
Tools like Fullstory and Google Analytics function as the core components in the machinery of data-driven decision-making, facilitating behavioral analytics.
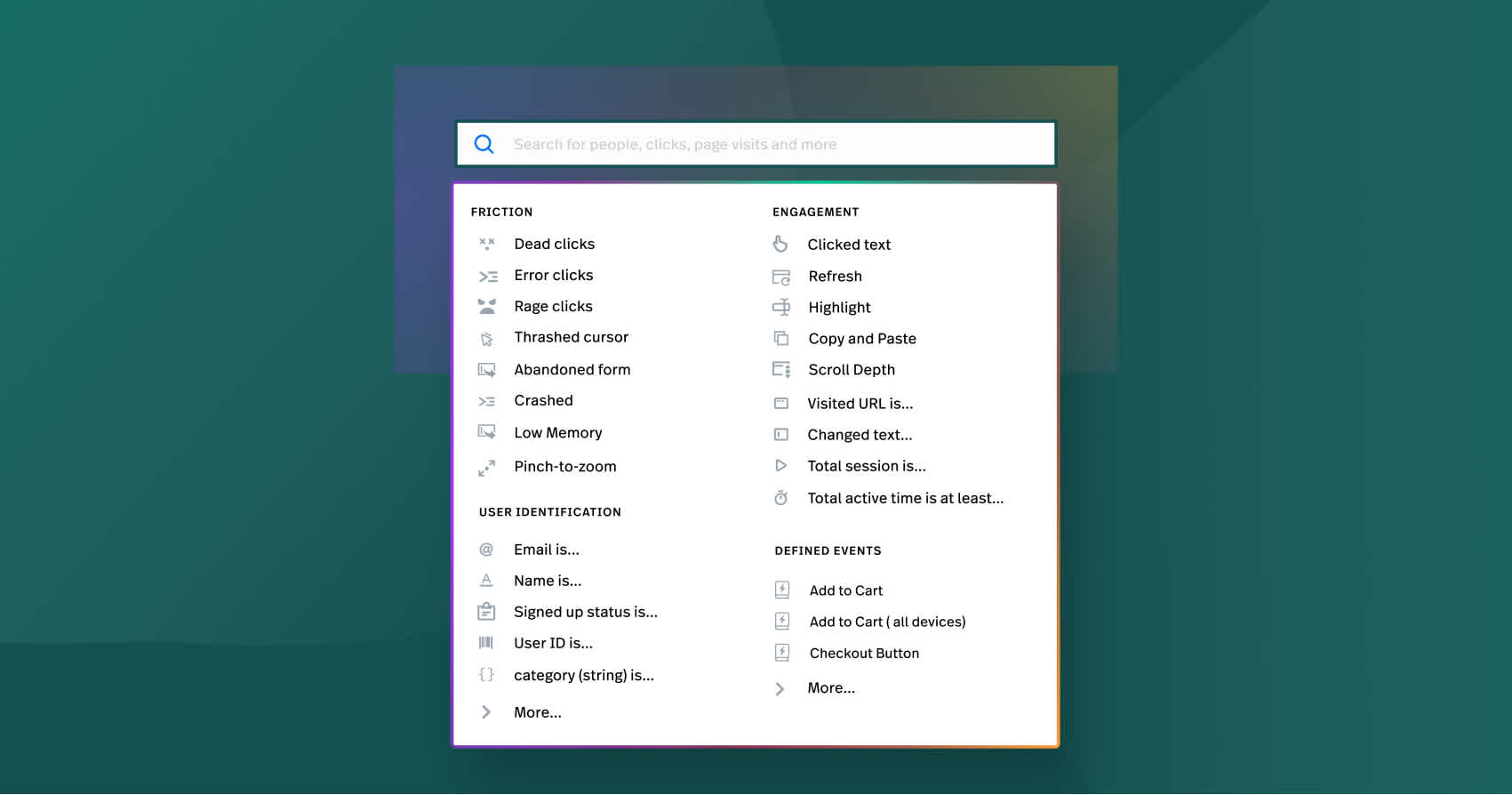
Google Analytics tracks user behavior across devices, offering detailed reports.
Fullstory deciphers hidden buying behaviors, equipping data teams to boost revenue with immediate personalization and predictive analysis. It surfaces the sentiment behind the clicks, aiding businesses in crafting superior experiences that secure lifelong loyalty.
These platforms specialize in providing insights into conversion, engagement, and retention without complex queries. Behavioral analytics tools employ advanced methods like cohort and funnel analysis to study user retention and conversion paths, enhancing customer experiences by combining qualitative feedback with quantitative data and tailoring offerings based on user activity metrics.
Behavioral data in marketing automation systems
Marketing automation systems utilize behavioral data as their powerhouse to craft personalized experiences for customers.
They trigger actions automatically following specific behaviors, thereby creating a seamless and personalized customer journey. By providing consistent messaging across multiple channels, these systems ensure a coherent brand presence, playing a vital role in customer acquisition in today’s multi-channel environment.
Behavioral data is instrumental in achieving business goals such as new customer acquisition, user retention, and minimizing churn rates. It builds trust and grows conversion rates.
Personalization campaigns that analyze customer behavior data like browsing history and purchase patterns allow marketers to send messages tailored to individual customer preferences. At the same time, segmentation enables more targeted and effective marketing strategies. This approach aligns closely with broader marketing analytics practices, enhancing overall campaign effectiveness.
Enhance user journey using customer data
Enhancing the customer journey stands out as a key application of behavioral data. It involves using personalization strategies, identifying friction points, and boosting user engagement to improve overall customer experience.
Let’s dive a bit deeper.
Personalization strategies
Personalization is no longer a luxury but a necessity.
Customers expect brands to understand their preferences and buying habits, and deliver personalized experiences. Organizations leverage behavioral data to understand customer behavior and create targeted segments, enhancing personalized marketing campaigns and improving customer experience.
Take Coca-Cola’s use of image recognition for targeted ads as an example.
This strategy has succeeded in increasing engagement, cautioning against over-personalization, and emphasizing the importance of allowing opt-out from personalized experiences. Product recommendations tailored to customers based on their past behaviors exemplify an effective personalization tactic contributing to increased interest and potentially higher sales.
Identifying friction points
Potential friction points, areas causing discomfort or frustration, are inherent in every customer journey. By analyzing behavioral data and surfacing the customer sentiment behind the clicks, businesses can work towards optimizing these friction points.
Behavioral data platforms like Fullstory offer the following benefits:
Collect data on user behavior patterns
Identify and alert about user friction in a user experience
Improve customer satisfaction and engagement
Lead to a more successful customer journey
Boosting user engagement
Boosting user engagement is a critical goal for many businesses, and behavioral data is often the missing link that breaks down the barrier to success.
Heatmap software, for instance, provides visual illustrations of user behavior on a website. These illustrations are critical in identifying areas that receive the most engagement and those that are ignored.
Feedback and voice of the customer tools offer insights that may not be apparent through quantitative data alone. Constantly enhancing the user experience based on insights from behavioral analytics plays a key role in fostering user loyalty and improving engagement.
Privacy and ethical considerations in behavioral data collection
As is true for any form of data collection, gathering customer behavior data carries its own privacy and ethical considerations. Behavioral tracking is governed by stringent regulations such as GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and PIPEDA in Canada, which mandate explicit consumer consent and the protection of personal information.
Around 40% of consumers lack trust in how brands handle their data, underscoring the urgent need for complete transparency and ethical practices in the use of behavioral data to prevent brand trust loss.
Practices like data manipulation or lack of transparency can lead to severe outcomes, including legal repercussions and fines, as well as a tarnished brand reputation.
Examples of businesses using behavioral data
To fully grasp the potential of behavioral data, let's consider some real-world examples.
Organizations leveraging behavioral data analytics see 85% more sales growth and a more than 25% increase in gross margin. By analyzing data, they can make informed decisions and optimize their strategies.

McDonald’s, for instance, has used behavioral data acquired from Dynamic Yield to optimize their high-volume business, effectively increasing customer satisfaction and sales.
DBS Bank’s investment in technology, including AI and data analytics, has transformed it into a data-driven organization, significantly improving the user experience.
Starbucks and Netflix have also benefited from the strategic use of behavioral data to tailor offers, shape product development, and strengthen customer relationships.
Applying behavioral data
Behavioral data unlocks the power of true personalization by revealing valuable insights into customer sentiment patterns.
By understanding your consumers' personalities through their actions, you can tailor your strategies to not just meet but match their moods, making every interaction deeply personalized and effective.
Improve customer engagement
Businesses use behavioral data to understand customer patterns such as page views and interactions. By analyzing how customers engage with digital platforms, companies can create personalized experiences.
Tools like recommendation engines leverage this data to suggest products, enhancing the customer's journey and interaction with the brand.
Data-driven product development
Insights into customer behavior significantly enhance product development. Companies leverage feedback and purchase patterns to refine new features or products. Integrating AI with a behavioral data platform further sharpens this targeted approach.
AI engines process and analyze data more deeply, revealing trends and sentiments that inform development strategies. This ensures efforts are not just aligned with, but also predictive of, actual customer preferences and needs, making development more responsive and tailored.
Optimize sales and marketing
Sales and marketing campaigns are tailored using predictive lead scoring and segmentation based on customer activity. This targeted approach can result in more effective campaigns and higher conversion rates. Marketing automation systems utilize behavioral data to fine-tune advertising and lead-generation strategies.
Enhance customer retention and loyalty
The analysis of customer interactions and purchase history informs strategies aimed at increasing lifetime value and reducing churn. Personalized email sign-ups and newsletter subscriptions are examples of how a Customer Data Platform (CDP) can foster loyalty and encourage repeat business.
By strategically applying behavioral data across various facets of a business, companies can enhance customer experiences, resulting in improved engagement, more efficient product development, and increased sales and customer loyalty.
Maximize impact with behavioral data
Behavioral data is pivotal today. It reveals customer preferences and guides marketing strategies. It enhances customer journeys and campaign effectiveness while upholding ethical standards.
Leveraging this data effectively drives informed decisions and business success.



